The next Bitcoin halving is a pivotal event in the cryptocurrency world‚ representing a pre-programmed reduction in the rate at which new Bitcoin enters circulation. This mechanism‚ embedded in Bitcoin’s core code‚ is designed to control inflation and maintain scarcity‚ a fundamental principle underpinning its value proposition. The anticipation surrounding the next Bitcoin halving often fuels market speculation and heightened investor interest‚ making it a crucial period to understand. This event‚ occurring roughly every four years‚ directly impacts Bitcoin miners‚ the reward they receive for validating transactions‚ and potentially the overall supply dynamics of the cryptocurrency.
Understanding the Halving Mechanism
Bitcoin’s halving process is a unique feature that distinguishes it from traditional fiat currencies. Unlike fiat currencies‚ which central banks can print at will‚ Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million coins. The halving ensures that the issuance of new Bitcoins gradually decreases over time‚ eventually reaching zero. This deflationary model is a key argument for Bitcoin as a store of value.
How Does Halving Work?
- Block Reward: Miners receive a certain amount of Bitcoin for each block of transactions they successfully add to the blockchain.
- Halving Event: Approximately every 210‚000 blocks (roughly every four years)‚ this block reward is cut in half.
- Reduced Supply: This reduction in the block reward effectively slows down the rate at which new Bitcoins are created.
Impact of Previous Halvings
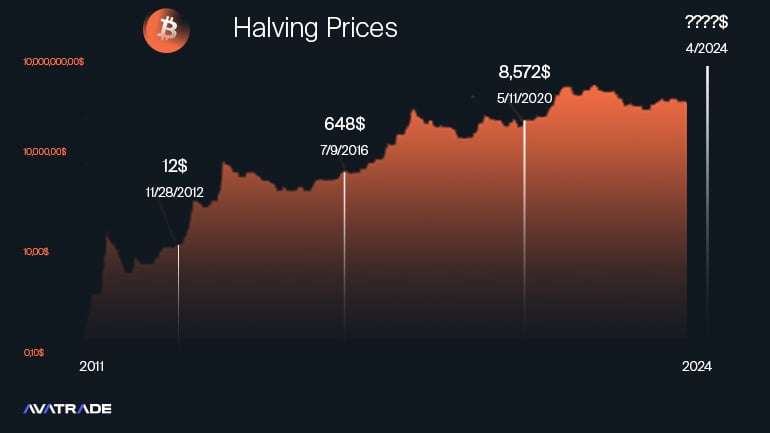
Historically‚ Bitcoin halvings have been associated with significant price appreciation‚ although correlation doesn’t equal causation. Analyzing past events can provide valuable insights into potential market behavior‚ but it’s crucial to remember that future performance is not guaranteed. Each halving occurs within a unique macroeconomic environment‚ and various factors can influence the market’s response.
A Look at the Numbers
| Halving Event | Date | Block Reward Before Halving | Block Reward After Halving | Approximate Price Change (Year After) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Halving | November 28‚ 2012 | 50 BTC | 25 BTC | Significant Increase (Highly Variable Estimates) |
| Second Halving | July 9‚ 2016 | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC | Significant Increase (Highly Variable Estimates) |
| Third Halving | May 11‚ 2020 | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC | Significant Increase (Highly Variable Estimates) |
Preparing for the Next Bitcoin Halving
The next Bitcoin halving presents both opportunities and challenges for investors and miners alike. Understanding the potential implications of the reduced block reward and its impact on market dynamics is essential for making informed decisions.
- For Investors: Consider your risk tolerance and investment strategy. Do your own research and consult with a financial advisor if needed.
- For Miners: Assess the profitability of your mining operations after the halving. Consider upgrading your hardware or exploring alternative revenue streams.
The upcoming event is surrounded by speculation‚ anticipation‚ and a complex interplay of market forces. The next Bitcoin halving represents a significant moment for the cryptocurrency ecosystem‚ and its effects will likely be felt throughout the market. By understanding the mechanics of the halving and its historical context‚ individuals can better navigate the evolving landscape of Bitcoin and its potential future.
POTENTIAL CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES POST-HALVING
While the halving is often viewed optimistically‚ it also presents potential challenges. A significant decrease in miner revenue could lead to some miners shutting down their operations‚ potentially impacting the network’s hash rate and security. However‚ this could also lead to a consolidation of the mining industry‚ with more efficient and well-capitalized miners gaining a larger share of the market.
POSSIBLE SCENARIOS:
– Miner Capitulation: Less profitable miners may be forced to sell their Bitcoin holdings to cover operational costs‚ potentially putting downward pressure on the price.
– Hash Rate Fluctuations: A decrease in the number of active miners could lead to slower block times and increased transaction confirmation times‚ at least temporarily.
– Price Volatility: The halving event itself‚ and the months following‚ are often characterized by increased price volatility as the market adjusts to the new supply dynamics.
– Renewed Investor Interest: The scarcity narrative reinforced by the halving could attract new investors to Bitcoin‚ potentially driving demand and price appreciation in the long term.
THE LONG-TERM VISION OF BITCOIN’S SCARCITY
The halving mechanism is a core component of Bitcoin’s long-term vision as a decentralized and censorship-resistant store of value. By gradually reducing the rate of new Bitcoin creation‚ the halving reinforces the digital asset’s scarcity and distinguishes it from traditional fiat currencies subject to inflationary pressures. This controlled supply‚ coupled with increasing adoption‚ is what many proponents believe will drive Bitcoin’s value over the long term.
As we approach the next Bitcoin halving‚ it’s crucial to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results. The cryptocurrency market is constantly evolving‚ and various factors can influence its behavior. However‚ understanding the underlying principles of the halving mechanism and its potential impact can empower investors and participants to make informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing landscape of digital finance. The next Bitcoin halving is a reminder of the planned scarcity of the cryptocurrency‚ a key element that defines its value proposition.