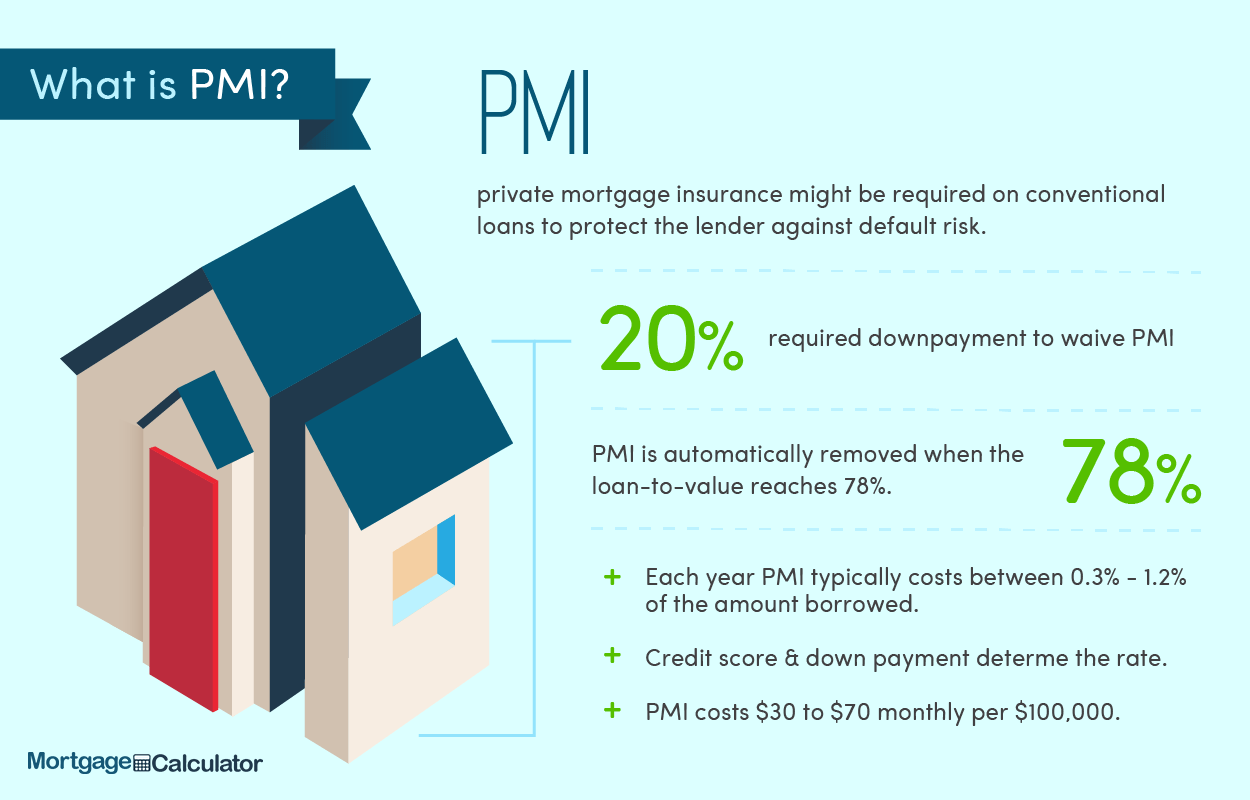
What is Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP)?
Mortgage insurance protects lenders if you default on your loan. For loans with less than 20% down payment, it’s often required. MIP is the premium paid for this protection, typically added to your monthly mortgage payment. Understanding MIP is crucial for budgeting and planning your home purchase.
Understanding the Basics of MIP
Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP) acts as a safety net for lenders, safeguarding them against potential losses if a borrower defaults on their mortgage loan. It’s essentially an insurance policy that protects the lender, not the borrower, from financial risk. This insurance is typically required when a borrower makes a down payment of less than 20% of the home’s purchase price. The smaller your down payment, the higher the risk for the lender, and consequently, the higher the MIP. Think of it as a fee for the added risk the lender assumes. The MIP is usually paid monthly and added directly to your mortgage payment, increasing your overall housing cost. It’s important to understand that MIP isn’t like homeowner’s insurance; it doesn’t cover damage to your property or liability. Its sole purpose is to protect the lender in case you fail to make your mortgage payments. It’s a crucial aspect of securing a mortgage, especially for first-time homebuyers or those with limited savings. Failing to understand MIP can lead to unexpected financial burdens, so it’s vital to thoroughly research and understand its implications before committing to a mortgage. Remember to factor MIP into your overall budget to avoid any financial surprises down the line. Proper budgeting and financial planning are key to successfully navigating the home-buying process and ensuring long-term financial stability.
Who Needs Mortgage Insurance?
Generally, borrowers who put down less than 20% of the home’s purchase price as a down payment will be required to pay for Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP). This is because a smaller down payment signifies a higher risk for the lender. The lender needs protection against potential losses should the borrower default on the loan. This requirement applies to both conventional loans and FHA loans, although the specific rules and types of insurance can differ. First-time homebuyers often fall into this category, as they may not have had the time to save a substantial down payment. Borrowers with lower credit scores might also find themselves needing MIP, as a lower credit score indicates a higher risk of default. Even with a good credit score, a smaller down payment will often trigger the MIP requirement. It’s crucial to understand that MIP is not solely determined by credit score; the loan-to-value ratio (LTV), calculated by dividing the loan amount by the home’s value, plays a significant role. Therefore, even borrowers with excellent credit might need MIP if their down payment is insufficient. It’s always advisable to consult with a mortgage lender to determine your specific needs and whether you’ll be required to pay MIP. Remember, understanding your eligibility for MIP is crucial for accurate budgeting and financial planning during the home-buying process. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and seek clarification from your lender to ensure a smooth and informed home-buying experience.
How is MIP Calculated?
The calculation of Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP) can vary depending on several factors, primarily the type of loan and the loan-to-value ratio (LTV). For FHA loans, the MIP is typically calculated as an upfront premium paid at closing and an annual premium added to your monthly mortgage payment. The upfront premium is usually a percentage of the loan amount, while the annual premium is expressed as a percentage of the outstanding loan balance. The exact percentages depend on the loan term and the borrower’s credit score. For conventional loans, the calculation differs slightly. Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI), the equivalent of MIP for conventional loans, is usually also calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. However, the percentage can vary based on the LTV and the borrower’s creditworthiness. Lenders often use a complex formula that considers various risk factors to determine the precise MIP or PMI amount. These factors can include the loan amount, the interest rate, the loan term, and the borrower’s credit history. It’s important to note that the calculation isn’t a simple, straightforward percentage; it’s a more nuanced process that takes into account the lender’s assessment of the risk involved. Therefore, it’s highly recommended to consult your lender or a mortgage professional for a precise calculation tailored to your specific circumstances. They can provide a clear and accurate breakdown of your MIP or PMI costs, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of your total monthly mortgage payment and overall financial obligations. Don’t hesitate to ask for clarification on any aspect of the calculation; understanding these details is crucial for responsible financial planning.
Factors Affecting Your MIP
Several key factors influence the amount you’ll pay for your Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP). Your loan-to-value ratio (LTV) is paramount; a lower LTV (meaning a larger down payment) generally results in a lower MIP or even eliminates the need for it entirely. The type of loan you choose significantly impacts your MIP. FHA loans, for example, typically have a higher MIP than conventional loans. Your credit score plays a crucial role; a higher credit score often translates to a lower MIP because it signals lower risk to the lender. The interest rate on your mortgage also affects the calculation, although not as directly as the LTV or credit score. A higher interest rate might indirectly influence the MIP by increasing the perceived risk. The length of your loan term is another factor; longer loan terms generally come with higher MIP costs due to the extended period of risk for the lender. Finally, the type of property you’re purchasing can also influence your MIP. Certain property types might be considered higher risk, leading to a higher MIP. It’s essential to understand these interconnected factors to effectively manage your MIP costs. Remember, a thorough understanding of these elements empowers you to make informed decisions during the mortgage process, potentially saving you substantial money over the life of your loan. Consulting with a mortgage professional can provide personalized insights and help you navigate the complexities of MIP calculations, ensuring you’re making the best financial choices for your unique situation. Don’t underestimate the impact these factors can have on your overall mortgage costs.